Circuit breakers are used in the following:
- In power plants and substations, they protect the main equipment from overloading, short circuit and thus, partial or total damage which costs very much.
- In branch circuits, they protect mainly the cables from overloading and breakdown also they protect the load from overloading in some cases.
- They protect you from leakage current in case of earth leakage circuit breakers. As in case you touched a live wire, the breaker senses the leakage current though your body to ground and then disconnects the circuit.
Types of circuit breakers
There are many types of CBs, here are some of them:
- Miniature Circuit Breaker: for low power applications and low short circuit level.
- Molded Case Circuit Breaker: can bear higher power up to 630 A and also can reach 100 kA as short circuit level.
- Air Circuit Breakers: used in many application in low voltage systems and is called Air as the insulating medium is Air.
- Vacuum Circuit Breaker: can bear higher voltages than the Air as it implements vacuum as the insulating medium and is used in medium voltage systems.
- Oil Circuit Breaker: used in medium and high voltage as oil is very robust insulating medium and has good capabilities in arc quenching.
- SF6 Circuit Breaker: the most common type and used in medium and high voltage due to the high dielectric strength of SF6, thermal stability and thermal conductivity.
Steps to Select a Circuit Breaker
- Determine load type to know which breaker suits your application. (Resistive, inductive o capacitive)
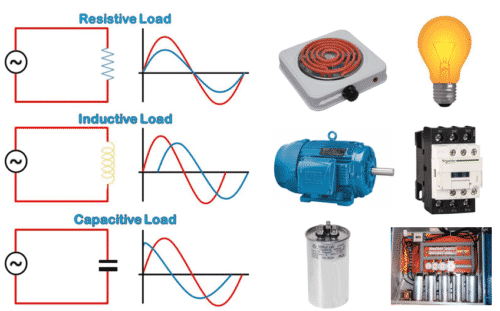
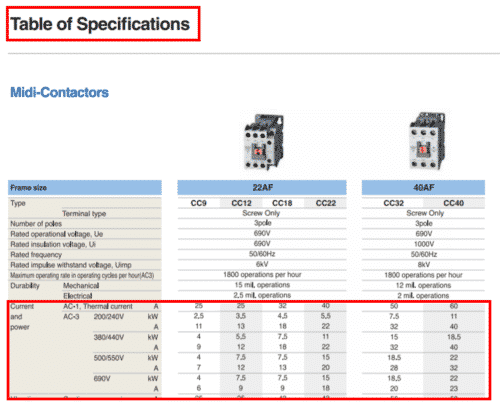
If you can’t identify the type of charge most of the components have something called Datasheet or Table of Specifications
Example:
In case of loads with starting current you should consider the circuit breaker magnetic trip current is higher than the starting current.
Example:
Electric motor
Typically, during the initial half cycle, the inrush current (starting current) is often higher than the normal full load current (running).
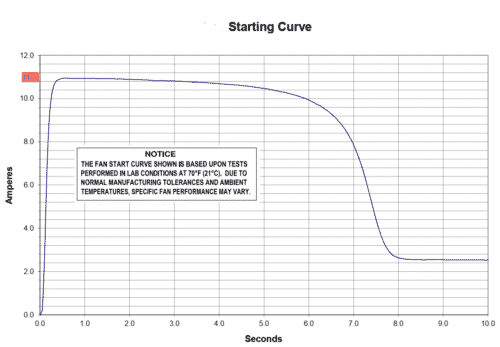
That is why is important to select a motor with starting curve included.
Motor:
2-From the Time Current Characteristic (TCC) graph of the selected breaker, find the multiple of rated current (M) by following the steps as defined below.
3-Identify the trip curve from your breaker
What is a trip curve?
A trip curve is a graphical representation of the expected behavior of a circuit protection device, trip curves plot the interrupting time of overcurrent devices based on a given current level. They are provided by the manufacturers of circuit protection devices to assist users with selecting devices that provide proper equipment protection and performance while avoiding nuisance tripping.
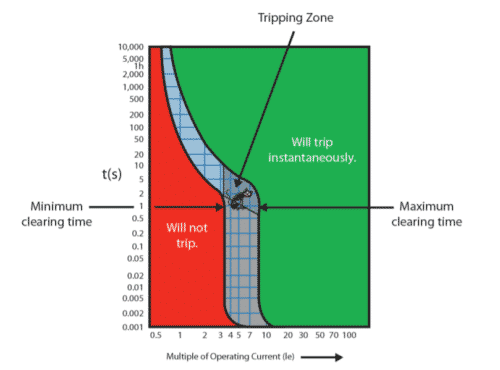
Take special note of the Tripping Zone where the breaker may or may not trip. Within the zone, until an overcurrent event happens, we do not know exactly when/if the breaker will trip or if the breaker will not trip.
Real example selecting a Circuit breaker
*For design, it is recommended to work under the tripping zone always verifying if the wire selected supports the current. (To calculate the wiring is important to verify the NEC, client specifications, company’s standards)
Data:
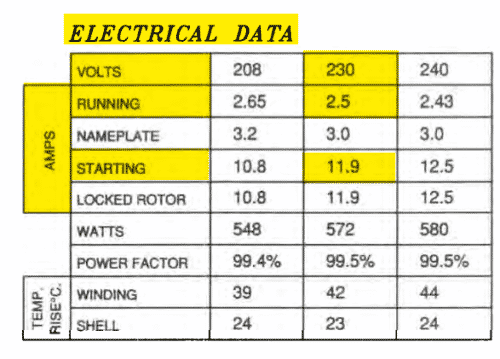
2 Motors
Rated Volts: 230V, Nameplate Rated current: 2.5A, Breaker K curve
So, Total Nameplate Rated current for the two motors =2.5*2=5 A.
Optional: Add a factor security depending of the standards of your project, for the protection purpose breaker should be selected 1.20 times the running current.
So, the required breaker rating is = 1.20*5= 6 A
In order to validate this breaker selected will withstand the short time duration inrush currents, following steps must be followed
Step A
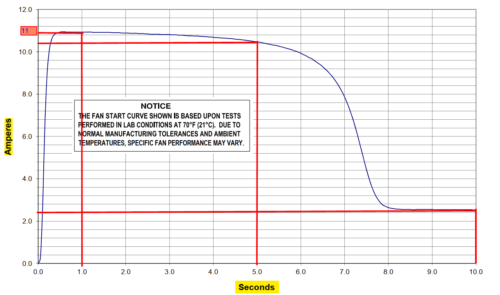
From the Time current curve of the motor, estimated short time currents are:
@1 sec is at 11A (see motor current/time graph) so Total inrush current for 2 motors = 11*2 I = 22A
@5 sec is at 10.5A (see motor current/time graph) so Total inrush current for 2 motors = 10.5A*2 I = 21A
@10 sec is at 2.4A (see motor current/time graph) so Total inrush current for 2 motors = 2.4A*2 I = 4.8A
Step B.
From the breaker’s Time current characteristics curve of the selected breaker shown above, the multiplication factor is as followed
1.2 times rated current for 10 seconds
1.4 times rated current for 5 seconds and
2.6 times the rated current for 1 second
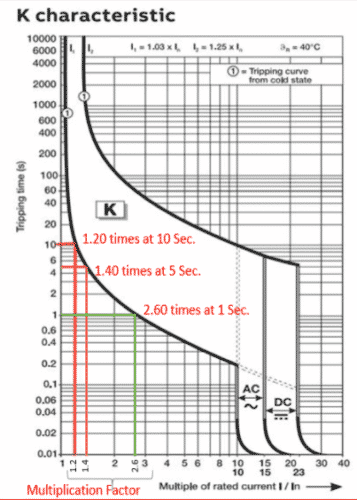
Therefore, Withstand capacity of breaker at 1 seconds = 2.6*6(Ampere rating of breaker) =15.6 A and 8.4A at 5 seconds and 7.2A and 10 second respectively.
Comparing the final values of step B with step A as shown below, it can be seen 6A breaker won’t be enough to withstand short time duration currents at 1 sec interval due to the motor short time current is higher than the Breaker withstand current.
| Time interval | Motor Short time current | Breaker Withstand Current |
| 1 Sec | 22A | 15.6A |
| 5 Sec | 21A | 8.4A |
| 10 sec | 4.8A | 5A |
Next available breaker rating is of 10 A
*Recalculate step B
Withstand capacity of breaker at 1 seconds = 2.6*10(Ampere rating of breaker) =26 A and 14A at 5 seconds and 12A and 10 second respectively.
| Time interval | Motor Short time current | Breaker Withstand Current |
| 1 Sec | 22A | 26A |
| 5 Sec | 21A | 14A |
| 10 sec | 4.8A | 10A |
Comparing the final values of step B with step A as shown below, it can be seen 10A breaker won’t be enough to withstand short time duration currents at 5 sec interval due to the motor short time current is higher than the Breaker withstand current.
Next available breaker rating is of 16 A
*Recalculate step B
Withstand capacity of breaker at 1 seconds = 2.6*16(Ampere rating of breaker) =41.6 A and 22.4A at 5 seconds and 12A and 19.2 second respectively.
| Time interval | Motor Short time current | Breaker Withstand Current |
| 1 Sec | 22A | 41.6A |
| 5 Sec | 21A | 22.4A |
| 10 sec | 4.8A | 19.2A |
Comparing the final values of step B with step A as shown below, it can be seen 16A breaker will be enough to withstand short time duration currents at 1,5 and 10 sec interval due to the motor short time current is higher than the Breaker withstand current.
*All the steps shown are for educational purposes, always revise the electrical code from your country to identify and select the correct components.
Posts related